
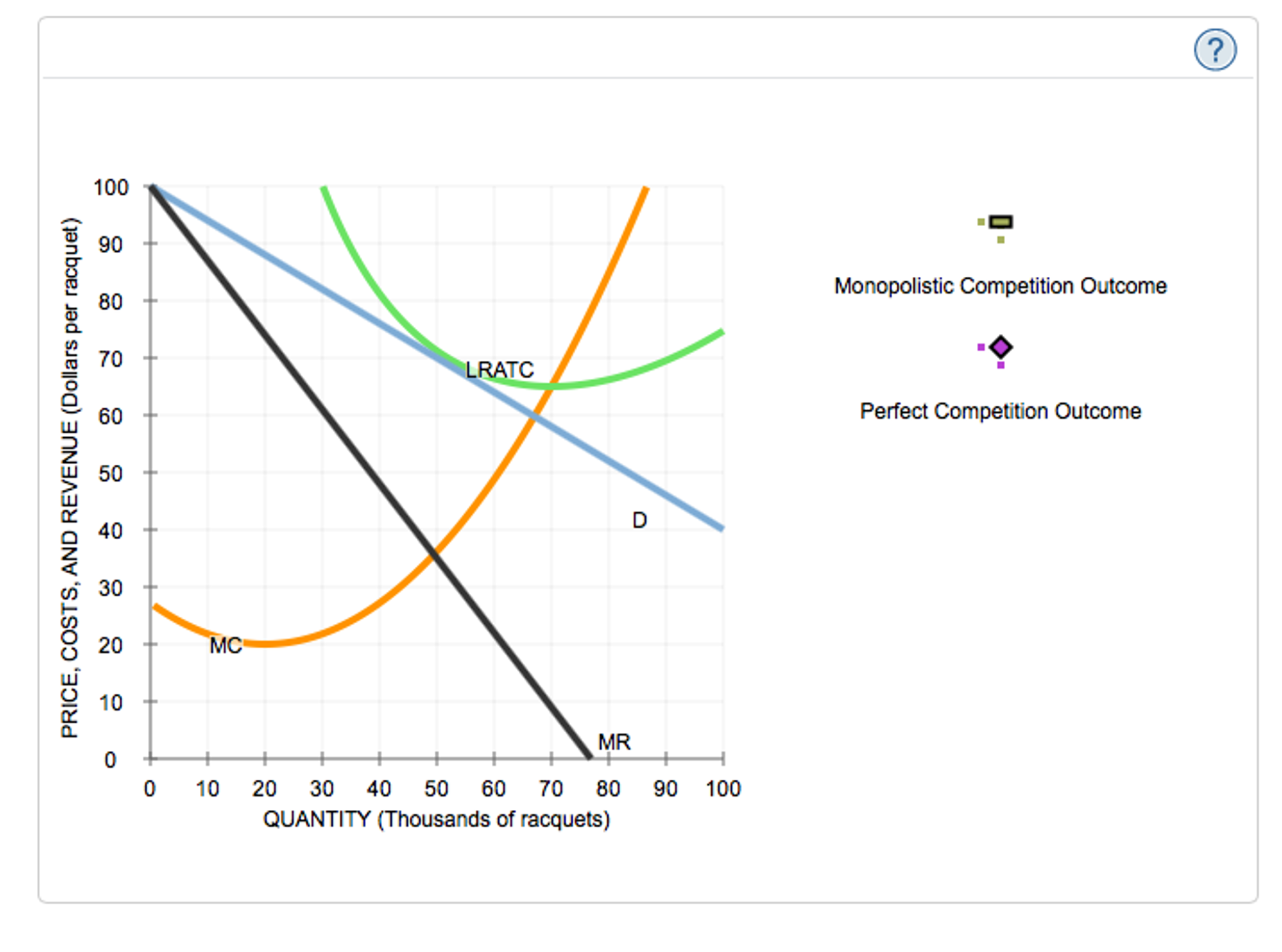
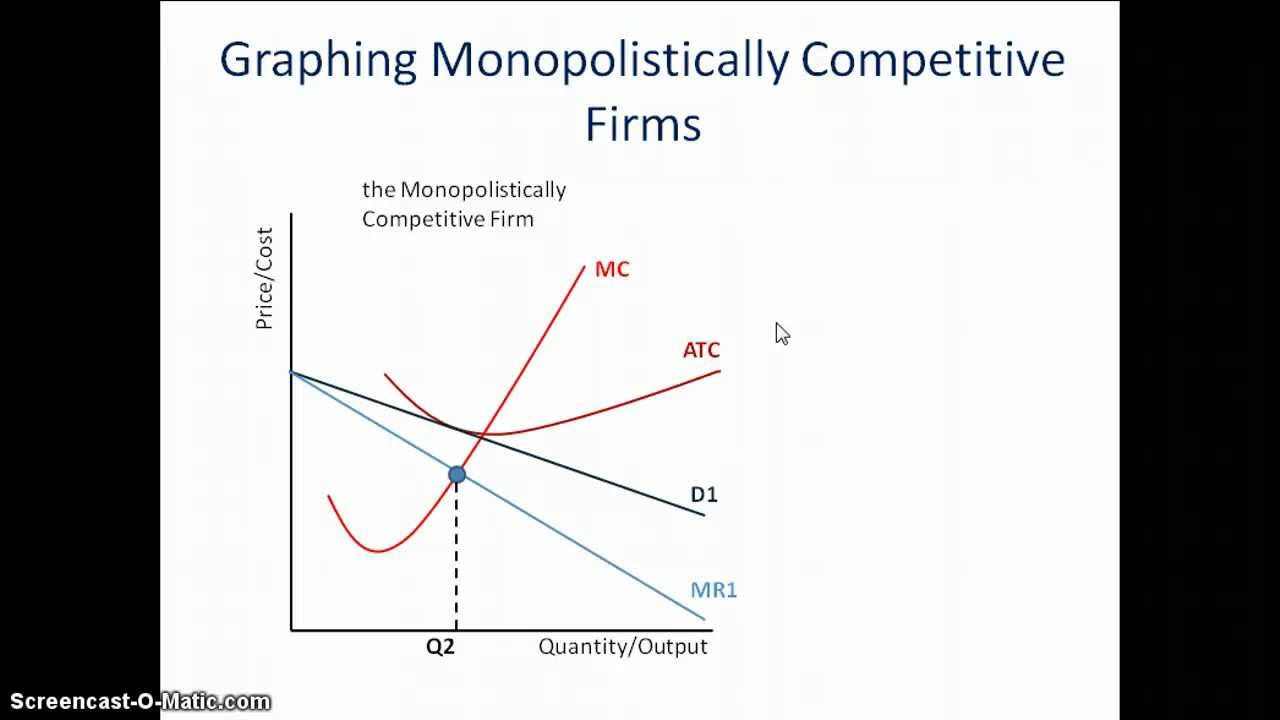
Long-run equilibrium of the firm under monopolistic competition. A short-run monopolistic competition equilibrium graph has the same properties of a monopoly equilibrium graph. The difference between the company's average revenue and average cost, multiplied by the quantity sold (Qs), gives the total profit. The company is able to collect a price based on the average revenue (AR) curve. The company maximises its profits and produces a quantity where the company's marginal revenue (MR) is equal to its marginal cost (MC). Short-run equilibrium of the company under monopolistic competition. The perfect competition forces each firm to either be efficient or perish or quit.Imperfect competition of differentiated products that are not perfect substitutes The average revenue curve of the monopolist is a downwards sloping curve.Įconomists are of this opinion that the monopolists are likely to be inefficient and slow in producing technological changes as compare to perfect competition. Therefore, variation of his output will cause variation in prices. The average revenue curve of the individual firm under perfect competition is therefore a straight line parallel to the X-axis. Therefore, he can sell as much or as little of his output as he chooses at the current price. The individual firm under perfect competition has an insignificant part of the industry and variation of its output does not affect prices. The supply curve of a firm under perfect competition is perfectly elastic. Hence, under Monopoly the marginal revenue is less than price. Therefore, if he wants to sell more he must reduce the price. But the Monopolist is by definition the sole producer. Variation of its output has no effect on prices and therefore marginal revenue is equal to price.
Under perfect competition the individual firm’s output is a small part of the total output.

In perfect competition Price = MC in monopoly P > MC. The firm determines the price and output. Under Monopoly there is no difference between firm and industry. The firms are price taker and output adjuster. The price is determined by the industry keeping in view the aggregate demand and aggregate supply. In a competitive market the number of buyers and sellers are large.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
